Technical Benefits
Field Test 4G Mobile Signal Strength
Want to know if Outdoor 4G Router works for you? Do a simple field test on your mobile phone by using your mobile phone to check the signal quality outside your house.
To get more accurate data, please disable the Wi-Fi connection on your mobile phone. You can read signal bars followed by carrier name and network symbol.
Mobile Network Types
You can see what network type you’re connecting to (2G, 3G, 4G, LTE, etc.). Take note of signal bars and the symbol in the status bar of your mobile phone and compare it with the below chart.
The 4G routers can connect to 2G, 3G, and 4G mobile networks. However, to get a fast speed and stable internet connection, we should input a robust 4G LTE signal for the router. For example, if the mobile symbol is G/E/3G/H, the 4G router can not work as well as it’s designed to. Please walk around to find another location that has the minimum 2-bar LTE signal reception.
| Symbol | Mobile Networks | Voice Call | Internet Speed | Email & Notification | Video |
| 4G (LTE) | Fourth generation or Long term evolution also known as LTE or WiMax |
Yes | 100Mbits/s+ | Yes | Yes |
| 3G | Third Generation also known as UMTS / WCDMA / CDMA2000 |
Yes | 2Mbits/s | Yes | Yes |
| 2G | GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) |
Yes | 50Kbits/s | Yes | No |
| E | EDGE (Enhanced Data GSM Evolution) |
Yes | 100Kbits/s | Yes | No |
| H/H+ | HSPA (High-Speed Packet Access) |
Yes | 10-100Mbits/s | Yes | Yes |
| No Symbol | If signal bars get more than 1 bar you can use voice call |
N/A | No | No | No |
Mobile Signal Quality
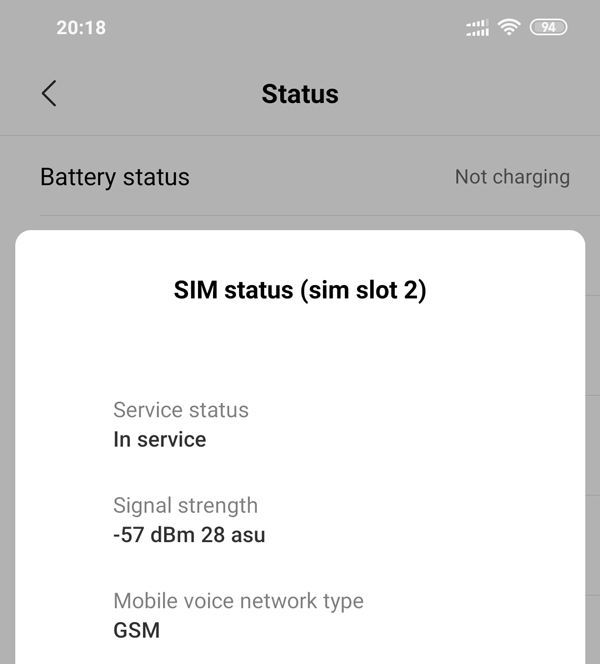
To measure mobile phone’s signal reception in exact decibels instead of bars or dots, you can follow guidance to enable the Field Test Mode in mobile phones.
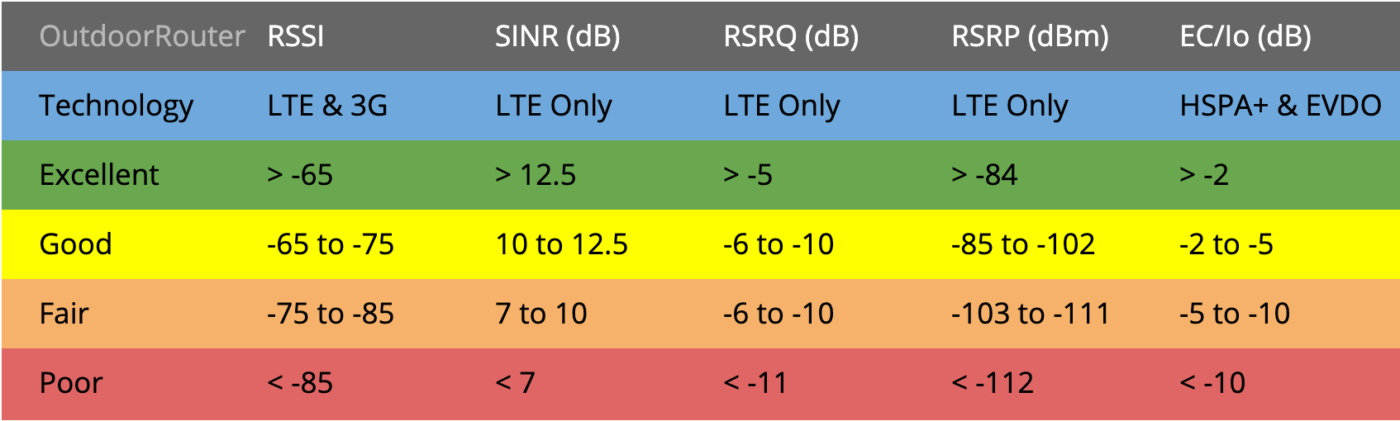
Decibel signal strengths will be negative 2~3 digits. Unit of measurement is dBm. If your phone show a number such as 98, the actual signal strength is -98dB. The closer the number is to zero, the better the reception, so -90dB is a stronger signal than -100dB.
The numerical value of 2G / 3G / 4G H+ networks is RSSI standard which is Received Signal Strength Indicator. LTE network is RSRP standard which is Reference Signal Receive Power.
Field Test Mode on iPhone

- Go into the Phone app and switch to the Keypad. Dial *3001#12345#* and press Call button to launch the Field Test Mode on your iPhone.
- In the iOS 14.8, tap the menu button on the top right corner.
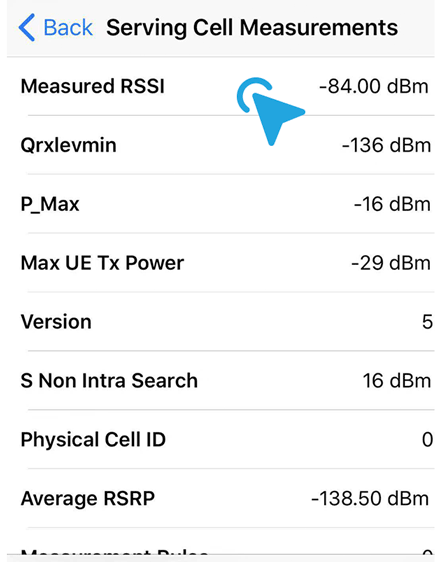
- Click Serving Cell Info, then nevigate to Freq_band_ind. That is the LTE frequency band.
- Return to the previous page and tap on Rach Attempt and find the RSRP value on the first row.
Field Test on iOS 14.8

- Go into the Phone app and switch to the Keypad. Dial *3001#12345#* and press Call button to launch the Field Test Mode on your iphone.
- In the iOS 13.3, tap on LTE > Serving Cell Info. Freq_band_ind is the LTE frequency band.
- Tap on Serving Cell Mass > Rsrp0 to check the LTE signal strength.
Field Test on iOS 13.3
Check Signals on 4G Router
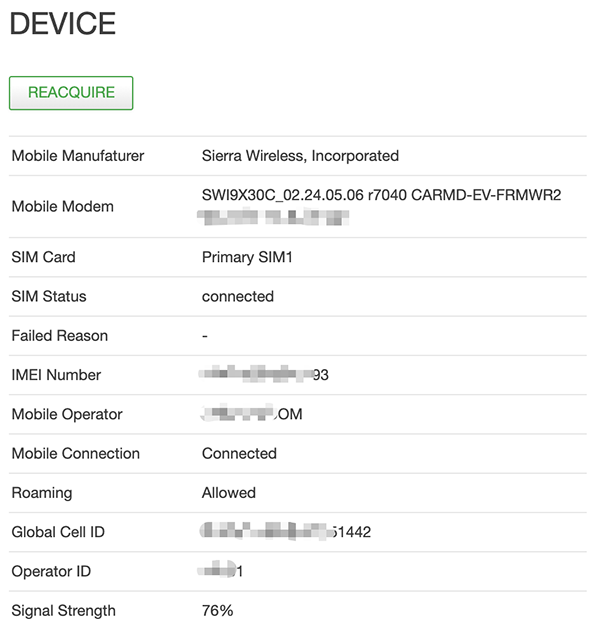
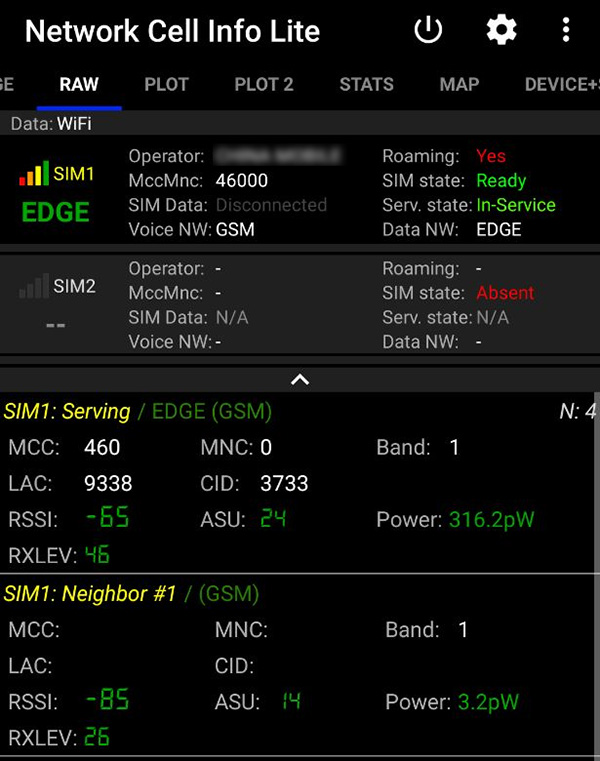
When the 4G router is turned on with a workable SIM card, log in the 4G router admin, we can find the modem device information on the right column of the front page.
The mobile modem model, IMEI number, and connection status are listed in the device column. Click the “Reacquire” button we can get the updated modem information.
Since EV3117 firmware version, the mobile protocol has switched to “MobileData”. The “Signal Strength” changed to a percentage number for easier understanding.
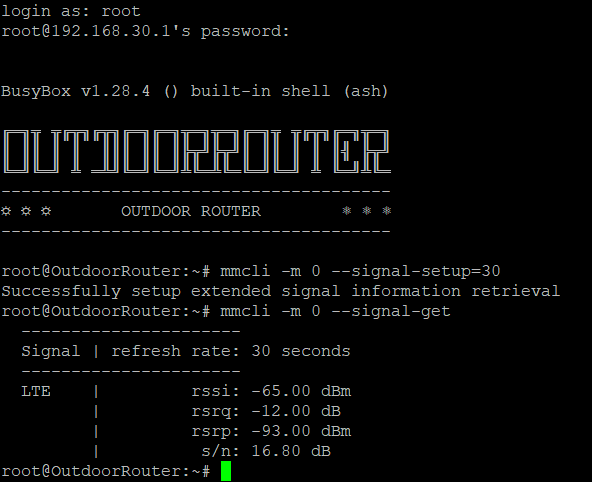
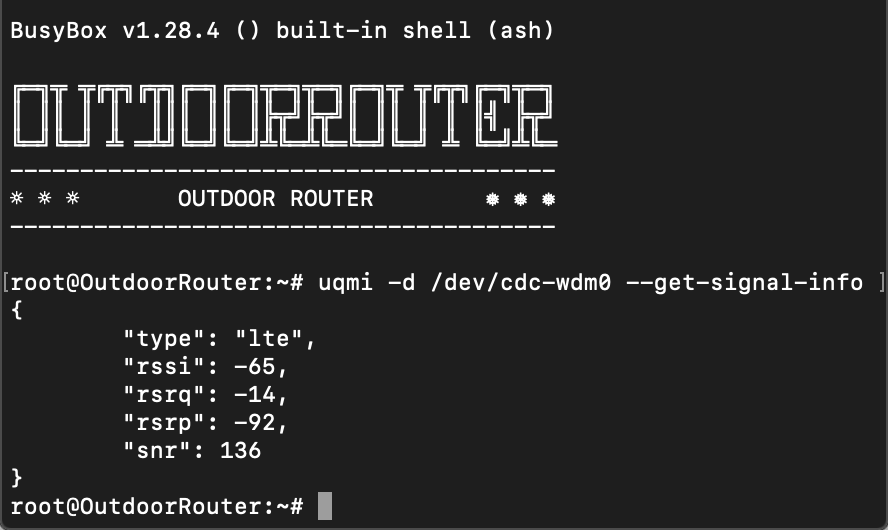
To read the exact decimal signal strength, please use the below MMCLI commands on SSH terminal.
SSH TERMINAL
After logging in the router admin, go to System > Terminal. Enter the router user name root and router password, which does not shows up when inputting, to enter the command-line interface on the web browser.
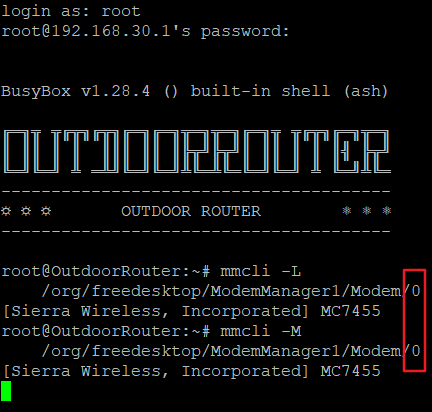
Verify Modem Sequence
mmcli -L
To list the current modem.
If the router has not set up a 4G connection, the guardian module will automatically restart the modem. The modem will disappear from the list temporarily. We can use the below command to monitor the modems.
mmcli -M
Press Ctr+Z on the keyboard to exit the monitor status.
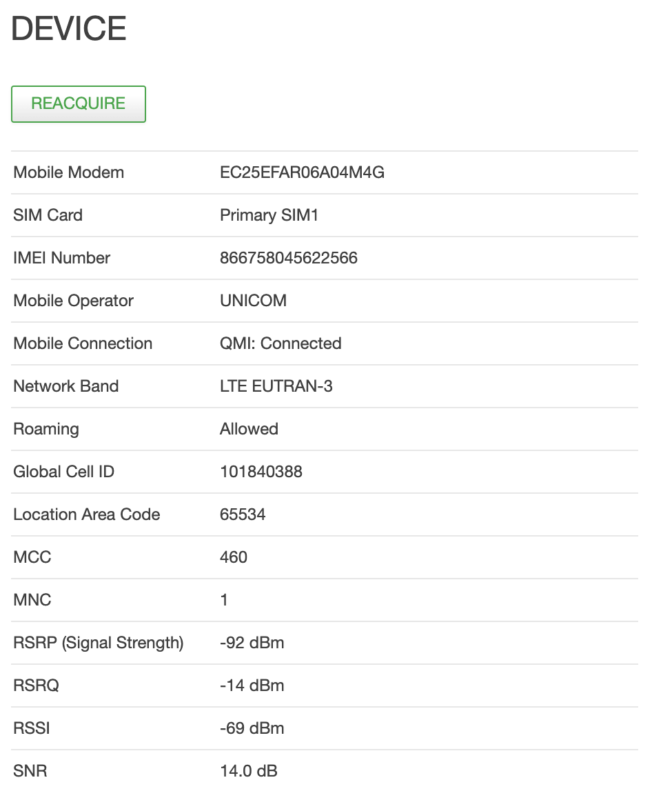
Insert a SIM card, turn on the power, and log in the 4G router admin. On the right column of the front page, you can check the modem device information, including mobile network band and signal strength.
Click the Reacquire button to get the updated signal strength information.
- The network band is the current mobile network connecting to.
- RSRP value is the signal strength. When connecting to 3G WCDMA or UMTS network, please check the RSSI value.
Since the mobile connection is in the first priority, on the first boot, the device information will take a few minutes to show completely.
SSH TERMINAL
After logging in the router admin, go to System > Terminal. Enter the router user name root and router password, which does not shows up when inputting, to enter the command-line interface on the web browser.
Verify SIM Registration
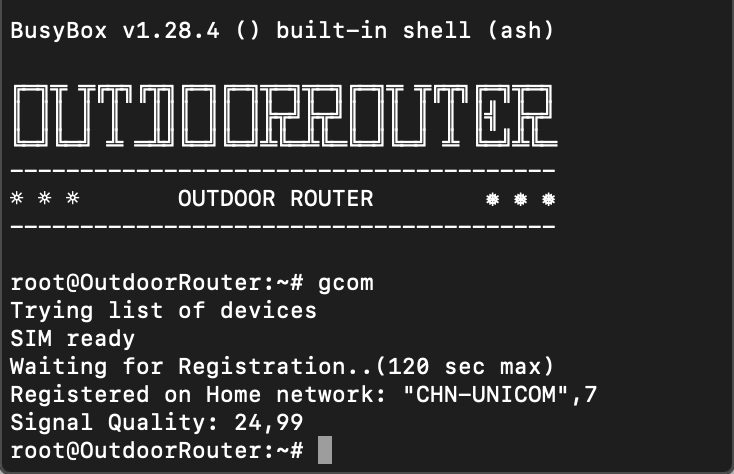
Enter gcom command to verify the SIM card installation and registration.
If it shows SIM error, please check if the SIM card is workable; if the SIM card inserts in the correct slot, the default setting is used SIM1 slot.
If the Registration is Failed, please check if the SIM card is already activated.
Signal bars VS decibel signal strength
| Signal Bars | iPhone Mobile | Nokia Phone |
| 5 | > -85 dBm | > -91 dBm |
| 4 | -85 ~ -90 dBm | -91 ~ -101 dBm |
| 3 | -90 ~ -95 dBm | -101 ~ -103 dBm |
| 2 | -95 ~ -100 dBm | -103 ~ -107 dBm |
| 1 | -100 ~ -105 dBm | -107 ~ -113 dBm |
| 0 | < -105 dBm | < -113 dBm |
4G LTE Bands and Frequencies
4G mobile phone networks has two different standards FDD LTE and TDD LTE. Both of them are used to maximize the available bandwidth.
FDD LTE uses a paired spectrum with different frequencies to transmitting (uplink) and receiving (downlink) signals simultaneously. TDD LTE uses unpaired spectrum because the working frequency for transmitting (uplink) and receiving (downlink) is exactly same.
| FDD-LTE Band | Uplink | Downlink | Band Width | Duplex Spacing | Guard Band |
| B1 | 1920 – 1980 MHz | 2110 – 2170 MHz | 60 MHz | 190 MHz | 130 MHz |
| B2 | 1850 – 1910 MHz | 1930 – 1990 MHz | 60 MHz | 80 MHz | 20 MHz |
| B3 | 1710 – 1785 MHz | 1805 – 1880 MHz | 75 MHz | 95 MHz | 20 MHz |
| B4 | 1710 – 1755 MHz | 2110 – 2155 MHz | 45 MHz | 400 MHz | 355 MHz |
| B5 | 824 – 849 MHz | 869 – 894 MHz | 25 MHz | 45 MHz | 20 MHz |
| B6 | 830 – 840 MHz | 875 – 885 MHz | 10 MHz | 35 MHz | 25 MHz |
| B7 | 2500 – 2570 MHz | 2620 – 2690 MHz | 70 MHz | 120 MHz | 50 MHz |
| B8 | 880 – 915 MHz | 925 – 960 MHz | 35 MHz | 45 MHz | 10 MHz |
| B9 | 1749.9 – 1784.9 MHz | 1844.9 – 1879.9 MHz | 35 MHz | 95 MHz | 60 MHz |
| B10 | 1710 – 1770 MHz | 2110 – 2170 MHz | 60 MHz | 400 MHz | 340 MHz |
| B11 | 1427.9 – 1452.9 MHz | 1475.9 – 1500.9 MHz | 20 MHz | 48 MHz | 28 MHz |
| B12 | 698 – 716 MHz | 728 – 746 MHz | 18 MHz | 30 MHz | 12 MHz |
| B13 | 777 – 787 MHz | 746 – 756 MHz | 10 MHz | – 31 MHz | 41 MHz |
| B14 | 788 – 798 MHz | 758 – 768 MHz | 10 MHz | – 30 MHz | 40 MHz |
| B15 | 1900 – 1920 MHz | 2600 – 2620 MHz | 20 MHz | 700 MHz | 680 MHz |
| B16 | 2010 – 2025 MHz | 2585 – 2600 MHz | 15 MHz | 575 MHz | 560 MHz |
| B17 | 704 – 716 MHz | 734 – 746 MHz | 12 MHz | 30 MHz | 18 MHz |
| B18 | 815 – 830 MHz | 860 – 875 MHz | 15 MHz | 45 MHz | 30 MHz |
| B19 | 830 – 845 MHz | 875 – 890 MHz | 15 MHz | 45 MHz | 30 MHz |
| B20 | 832 – 862 MHz | 791 – 821 MHz | 30 MHz | – 41 MHz | 71 MHz |
| B21 | 1447.9 – 1462.9 MHz | 1495.9 – 1510.9 MHz | 15 MHz | 48 MHz | 33 MHz |
| B22 | 3410 – 3500 MHz | 3510 – 3600 MHz | 90 MHz | 100 MHz | 10 MHz |
| B23 | 2000 – 2020 MHz | 2180 – 2200 MHz | 20 MHz | 180 MHz | 160 MHz |
| B24 | 1625.5 – 1660.5 MHz | 1525 – 1559 MHz | 34 MHz | – 101.5 MHz | 135.5 MHz |
| B25 | 1850 – 1915 MHz | 1930 – 1995 MHz | 65 MHz | 80 MHz | 15 MHz |
| B26 | 814 – 849 MHz | 859 – 894 MHz | 35 MHz | 45 MHz | 10 MHz |
| B27 | 807 – 824 MHz | 852 – 869 MHz | 17 MHz | 45 MHz | 28 MHz |
| B28 | 703 – 748 MHz | 758 – 803 MHz | 45 MHz | 55 MHz | 10 MHz |
| B29 | N/A | 717 – 728 MHz | 11 MHz | N/A | N/A |
| B30 | 2305 – 2315 MHz | 2350 – 2360 MHz | 10 MHz | 45 MHz | 35 MHz |
| B31 | 452.5 – 457.5 MHz | 462.5 – 467.5 MHz | 5 MHz | 10 MHz | 5 MHz |
| B66 | 1710 – 1780 MHz | 2110 – 2200 MHz | 90/70 MHz | 420 MHz | 330 MHz |
| B71 | 663 – 698 MHz | 617 – 652 MHz | 35 MHz | -46 MHz | 11 MHz |
| TDD-LTE Band | Frequency | Band Width |
| B33 | 1900 – 1920 MHz | 20 MHz |
| B34 | 2010 – 2025 MHz | 15 MHz |
| B35 | 1850 – 1910 MHz | 60 MHz |
| B36 | 1930 – 1990 MHz | 60 MHz |
| B37 | 1910 – 1930 MHz | 20 MHz |
| B38 | 2570 – 2620 MHz | 50 MHz |
| B39 | 1880 – 1920 MHz | 40 MHz |
| B40 | 2300 – 2400 MHz | 100 MHz |
| B41 | 2496 – 2690 MHz | 194 MHz |
| B42 | 3400 – 3600 MHz | 200 MHz |
| B43 | 3600 – 3800 MHz | 200 MHz |
| B44 | 703 – 803 MHz | 100 MHz |



Hi, this command line
mmcli -m 0 –signal-get
doesn-t give me info about the signal as in the screenshot.
It return only general informations about the router.
I-ve got a double directional antenna, and I would like to find to best orientation. But no matter what direction I-m pointing it-s always the same signal strength showing in the “modem device information on the right column of the front page”
Have you set up the time interval with the command of “mmcli -m 0 –signal-setup=30”? Could you email us the return message of “.. -signal-get”? Refresh the web page you will get the latest signal information on the front page.
Yes I did set up the time interval. Which email can I send you the message I’ve got? Thanks for your help.
Here are the 2 correct command lines :
mmcli -m 0 --signal-setup=20mmcli -m 0 --signal-getHello
I am in the rare case where I need to lock the 4g router on a specific band to achieve a stable connection. But I dont understand how to get the list of the bands that the modem received to be able to lock the modem to one of these bands.
thanks
You can refer to the tutorial to lock 4G LTE bands on the SSH terminal.
Hi
I tried to connect to the link that allows me to change the frequency bands through SSH, but the link doesn’t work. Can you please proved working link. Can you also proved a list all of the SSH commands?
I have the issue. Used mmcli -L command to confirm that using Modem 2.
I then ran the command (which differs from your tutorial and the screenshot) mmcli -m 2 –signal-get
I get the error: modem had no extended signal capabilities
The Device status on the Status Overview page does not show any detail on the SIM connection apart the operator. It says SIM status – disabled. I am unable to see any signal strength details inc. which technology i.e. 4G LTE I am using…..
Currently using firmware version EV3121. Router model EZR33.
Please set up the signal capture interval before execute –signal-get. The command to set up the 30 seconds interval is “mmcli -m 0 –signal-setup=30”.
I cannot connect anymore. I have tried the commands but on:
mmcli -m 0 –signal-get
I get:
error: modem has no extended signal capabilities
Also, when I press Ctrl+Z it says:
^Z[1]+ Stopped mmcli -M
which I’m not sure it’s correct. Normally to stop something I do Ctrl+C. Ctrl+Z stops it. Are we sure is this what we want?
Please use “mmcli -L” to check the active modem sequence. It might be using a larger sequence number rather than 0.
Thanks for the update
The “CHECK SIGNALS ON 4G ROUTER” section seems to be out of date wrt Firmware Version EV3117 (at least on the EZR53 device)
Thank you for your advice. Please check the updated tutorial under the tab of ≥ EV3117.